Job-Site OSHA Construction Standards

Last updated November 12, 2024
OSHA has construction industry standards on everything from hazardous chemical storage to underwater diving or crane operation.
Below are a few guidelines related to OSHA’s Top 10 Violations and simple explanations of the requirements. Please refer to your OSHA standards handbook or the OSHA website for the full, legal guidelines.
Table of Contents
Do OSHA Construction Standards Apply to General Industry?
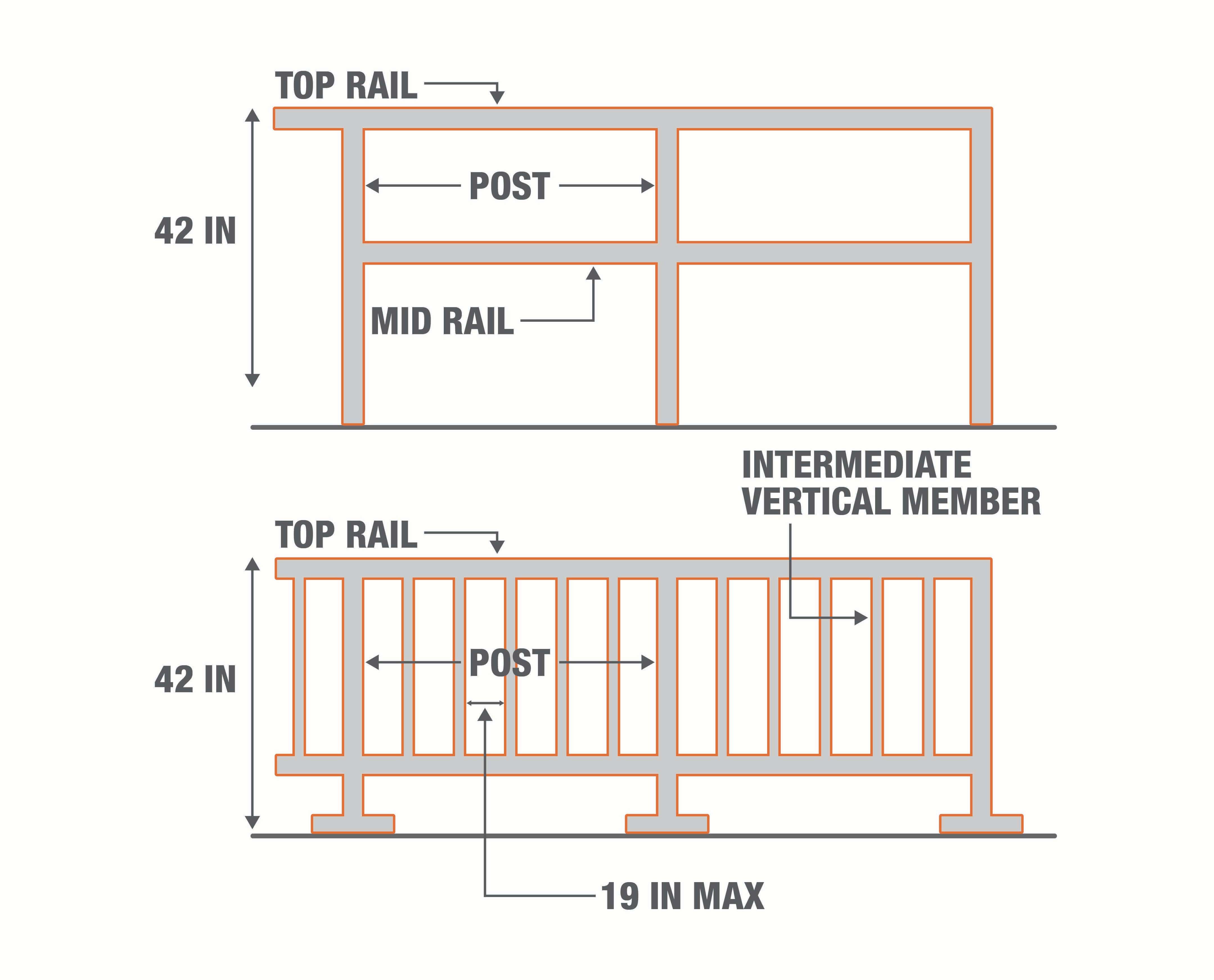
Fall Protection (1926.501)
Hazard Communication (1926.59)
Scaffolds (1926.451)
Lockout / Tagout (1926.417)
Respiratory Protection (1926.103)
Do OSHA Construction Standards Apply to General Industry?

OSHA construction standards (29 CFR Part 1926) apply to construction tasks regardless of industry. Construction is regarded as the alteration, renovation or construction or a new system or feature. Where there is not a specific construction requirement, employers should follow OSHA’S general industry guidelines.
Fall Protection (1926.501)

Acceptable fall protection includes guardrail systems, personal protection equipment or safety nets. Fall protection equipment is required for employees working at least 6 feet above a lower level, including:
- Hoist areas
- Excavations 6 feet deep or more
- Dangerous equipment 6 feet or less from employees
- Steep roofs with unprotected sides or edges
- Precast concrete fixtures, such as beams or wall panels
- Residential construction
- Wall openings
Additional safety nets or personal protection may be required for employees more the 6 feet above dangerous equipment.
Holes in the working surface, such as skylights, must be covered to protect employees from trips and falls or falling objects.
Hazard Communication (1926.59)

The OSHA construction standards for hazard communication are identical to the general industry standards (CRF 1910.1200).
Hazard communication includes container labeling, safety data sheets, employee training and lists of chemical hazards in the workplace. It is important for employers to keep a written hazard communication plan, ensure containers are labelled and distribute safety data sheets.
Your written hazard communication plan should include a:
- List of hazardous chemicals in the workplace
- Method to inform personnel of non-routine hazards, like cleaning or disinfecting
Your hazard communication plan should be kept at the primary work facility. The plan must include additional details if there is a risk that personnel of other employers, such as subcontractors, may be exposed to the chemical hazards.
Scaffolds (1926.451)
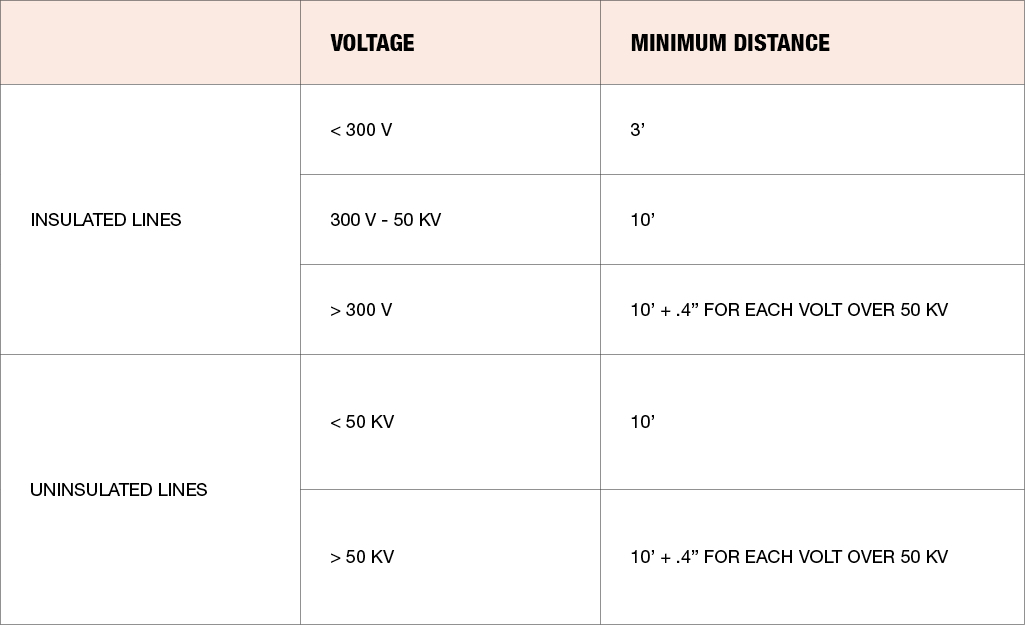
If your work site is near power lines, the minimum required distance for scaffolds is determined by the type of line.
Use the graph above to determine the correct distance for your team's safety.
When using scaffolds on the job site:
- Do not load them past the maximum intended load.
- Do not use shore or lean-to scaffolds.
- Inspect for defects before each work shift.
- Repair or replace any damaged part of a scaffold immediately.
- Only move or dismantle scaffolds under direction of qualified personnel.
Work on scaffolds should be avoided during storms or high winds, and personnel should not use any equipment covered in debris or ice. Additionally, fall protection is required for employees working on a scaffold 10 feet or more above the lower level. This is a few feet above the 6-foot fall protection standards for workers who do not have a support of a scaffold.
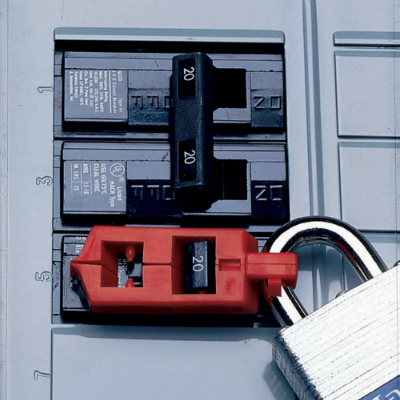
Lockout / Tagout (1926.417)

Electrical equipment or circuit breakers scheduled for maintenance must be deenergized and inoperable. All controls on the equipment or circuits that will be deactived in the course of work must be tagged. Lockout kits should be used to keep the equipment off, and tags must attached at all points to identify the equipment being worked on.
Respiratory Protection (1926.103)

The OSHA construction industry respiratory protection requirements are identical to the general industry requirements (1910.134).
It is the responsibility of the employer to develop and implement a written respiratory protection plan. The plan must include:
- Procedures for selecting protection for the workplace
- Medical evaluations of employees required to wear respirators
- Fit testing procedures for tight-fitting respirator masks
- Proper use guidelines for respirators in routine and emergency circumstances
- Employee training on respiratory hazards in the workplace and PPE usage
It is also the employer’s responsibility to select a National Institue for Occupational Safety and Health-certified respirator appropriate to the workplace hazards. A hazard assessment should be conducted to determine the kind of PPE necessary, as well as evaluations of the employees who will be required to wear it.
All respirators must fit employees closely and seal to the face. If an employee wears prescription glasses or has other medical requirements, the PPE must fit over the glasses or incorporate the prescription. Employers should change the cartridges in respirators as often as necessary to maintain effectiveness and encourage employees to wash their faces and hands when leaving the hazard area.
Ladders (1926.1053)

When using ladders on the job site:
- Keep them clean of grease, ice or other slipping hazards.
- Ladder rails should extend 3 feet or more past the landing surface. When such extension is not possible, the ladder must be secured at the top with a stabilizer and a grab rail must be provided.
- Do not load the ladder past intended maximum load.
- Do not use the top of the ladder as a step.
- Keep areas around the top and bottom of the ladder clear.
- Use only on stable and level surfaces, and provide slip-resistant feet on slick surfaces.
Ladders should not be tied or fashioned together to extend the length unless they were manufactured for such purpose. Never move or shift a ladder while in use.
Fall Protection – Training Requirements (1926.503)

Training must be provided for any personnel that may be exposed to a fall hazard. This training must be recorded with a written certification containing the date, personnel signature and employer or trainer signature. Retraining may be required when there is a change in the workplace or current fall protection systems. Training should include:
- Fall hazards in the workplace
- Proper procedures erecting, maintaining and inspecting fall protection
- Safe usage of fall protection, including guardrail systems, safety nets and personal protection
- Limitations of mechanical equipment on low-sloped roofs
- Proper storage and handling of equipment and materials
Eye & Face Protection (1926.102)

OSHA-approved eye protection must comply with American National Standards Institute Z87.1 standards from 1989, 2003 or 2010. Eye and face protection is required to protect from:
- Flying particles
- Molten metal
- Liquid chemicals
- Acids or caustic liquids
- Chemical gases or vapors
- Potentially injurious light radiation
Safety glasses with side protection are required for flying object hazards, and the manufacturer must be clearly marked on PPE. All employees who wear prescription glasses must have eye protection that can be worn over glasses or incorporates the prescription.
More specific eye and face protection is required for welding or exposure to laser beams.
Who Needs OSHA Construction Training?

OSHA Construction training is required for personnel who work on construction, alteration and repair, including painting and decorating. Training needs are determined by the type of work the employee will do on a day-to-day basis and often cover general safety and health guidelines, personal protective equipment and fall protection. Maintenance workers do not need OSHA construction training.
Which set of regulations an employer needs to follow may vary by job. All construction tasks are regulated under 29 CFR 1926 Construction Industry Standards while repair and maintenance are regulated under 29 CFR 1910 General Industry Standards.
Whether a job is considered construction or maintenance also depends on the scale and complexity of the task.
DEFINTIONS
Construction: Work for construction, alteration and/or repair, including painting and decorating
Maintenance: Keeping structures, fixtures or equipment working in the existing state
EXAMPLES
Construction
- Stripping and repainting a building facade
- Installing a new bathroom sink
- Replacing a utility pole with an improved pole
Maintenance
- Scheduled repainting in a rental unit
- Removing and replacing press fittings
- Replacing a utility pole with an identical pole
More Tools. More Products. More Perks.

Be more competitive and boost your bottom line with Pro Xtra, The Home Depot’s loyalty program built for Pros. Sign up today to access the enhanced Pro Online Experience, built with the online business tools and time-saving features Pros need.
Authorize employee in-store purchases quickly and securely via text. When Pro Xtra members enroll in Text2Confirm, you have total visibility to a details list of everything your employee is buying.
The information provided in this brochure does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal advice; instead, all content is for informational purposes only.
This brochure does not create an attorney-client relationship between the reader and The Home Depot Pro. You should consult your attorney to obtain advice with respect to any particular legal issue or problem.