Types of Vents

Last updated September 7, 2023
Vents are the network of rectangular, round and oval ducts that branch through the walls, floors and ceilings, and are designed to continuously control the humidity, freshness and comfort level of the air in your home. Properly connected and insulated, the ducts in your home can provide significant levels of comfort as well as energy efficiencies that can lower your heating and cooling costs.
This guide will help you understand how venting works in your home and offer solutions to help you get the most out of your venting system.
Table of Contents
Venting Types
Duct Design & Materials
Common Duct and Vent Sizes
Insulation & R-Values
Insulation Type
Upkeep & Features
Venting Types
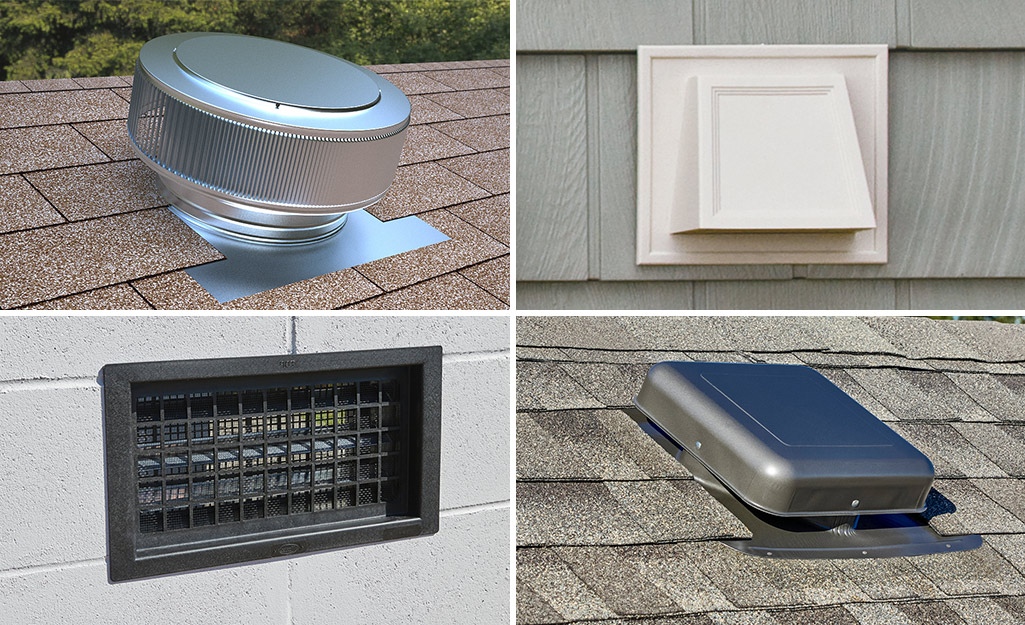

There are three types of venting in your home: venting for supply air, return air and exhaust air. The effectiveness of these venting systems is facilitated by a combination of heating and air system materials, duct sizes, duct sealant and insulation.
- Return Air: Air that has circulated through your home as supply air and is returned to the HVAC system for additional conditioning or release from home. Return ducts help pull air into vents that is being pushed in by supply ducts.
- Supply Air: A mixture of recirculated and outside air which has been conditioned and delivered into your home. This can be either 100 percent recirculated air, 100 percent outside air or any mixture of the two.
- Return Air: Air that has circulated through your home as supply air and is returned to the HVAC system for additional conditioning or release from the home. Return ducts help pull air into vents that is being pushed in by supply ducts.
Tip: Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERV) and Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRV) can help reduce energy costs of heating/cooling the incoming supply air by treating it with their own heat exchanger systems.
Duct Design & Materials
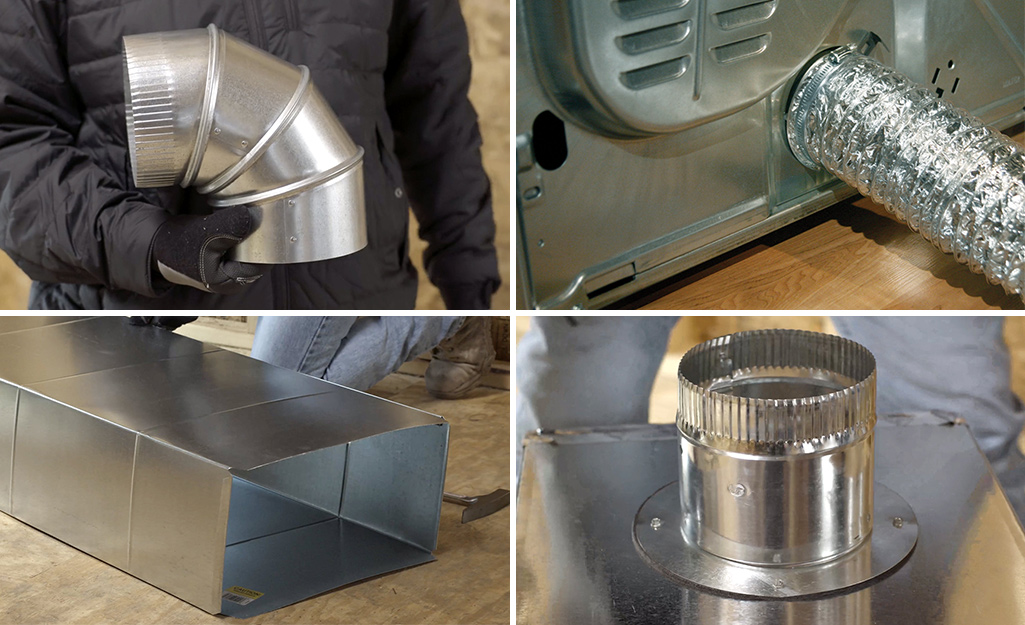

Ducts can be made from galvanized steel, fiberglass duct board/insulation panels or flexible ducting. They are available in a range of sizes, but ducts, in-wall stacks and registers, have standard sizes commonly found in homes.
Here are some common materials used in ducts and vents:
- Metal ducts are made from galvanized steel and can be wrapped or lined with fiberglass insulation. It also cuts and bends easily.
- Plenums and Air Returns is made from fiberglass duct boards and can be constructed with built-in thermal insulation, can be cut into various shapes and dampens sound.
Flexible ductwork is made from flexible ducting. They are often round and covered with a thin layer of plastic over fiberglass insulation. Flexible ductwork works best with minimized turns and in lengths of 15 feet or less.
Common Duct and Vent Sizes
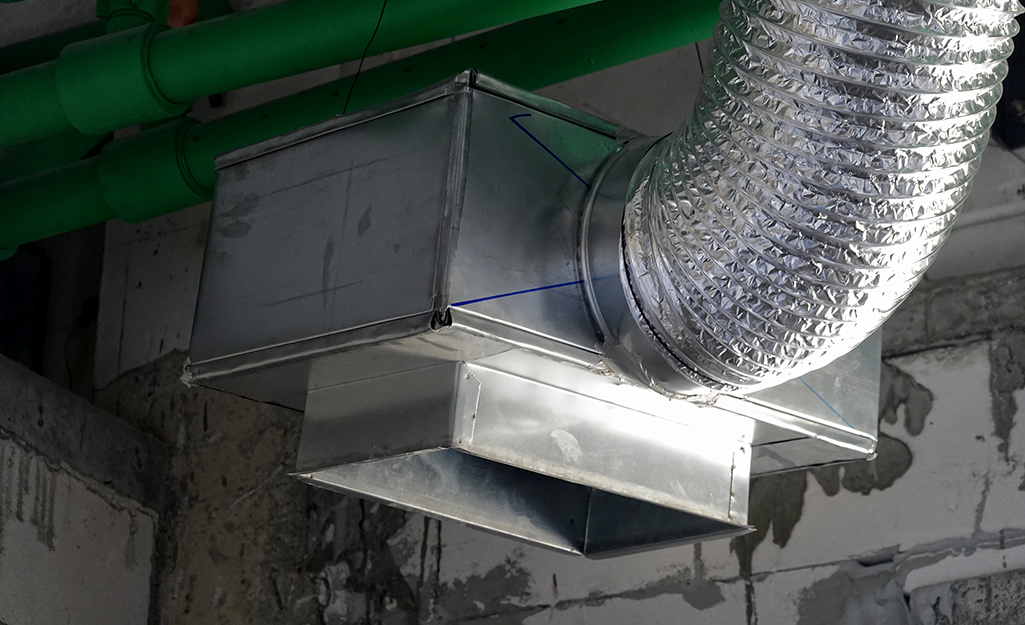

Here are a few sizes:
- Ducts: 4, 5, 6, 7 or 8 inches
- In-wall stacks: 3 1/4 x 10 inches, 3 1/4 x 12 inches or 3 1/4 x 14 inches
- Registers: 4 x 10 inches, 6 x 10 inches, 4 x 12 inches, 6 x 12 inches
Insulation & R-Values
- Insulating ducts in unconditioned spaces increases energy efficiency and prevents condensation from forming, so you can avoid problems with mold and mildew.
- Return air ducts only need to be insulated if they pass through environments that adversely affect the return air temperature.
- Supply air ducts don’t require insulation if they run exposed through the space being conditioned.
- Exhaust air ducts normally do not need insulation.
Insulating your ducts can be a simple project for DIYers. Sheets are cut to fit and attached to one another with high-quality foil tape or other attachment mechanisms.
Insulation Type
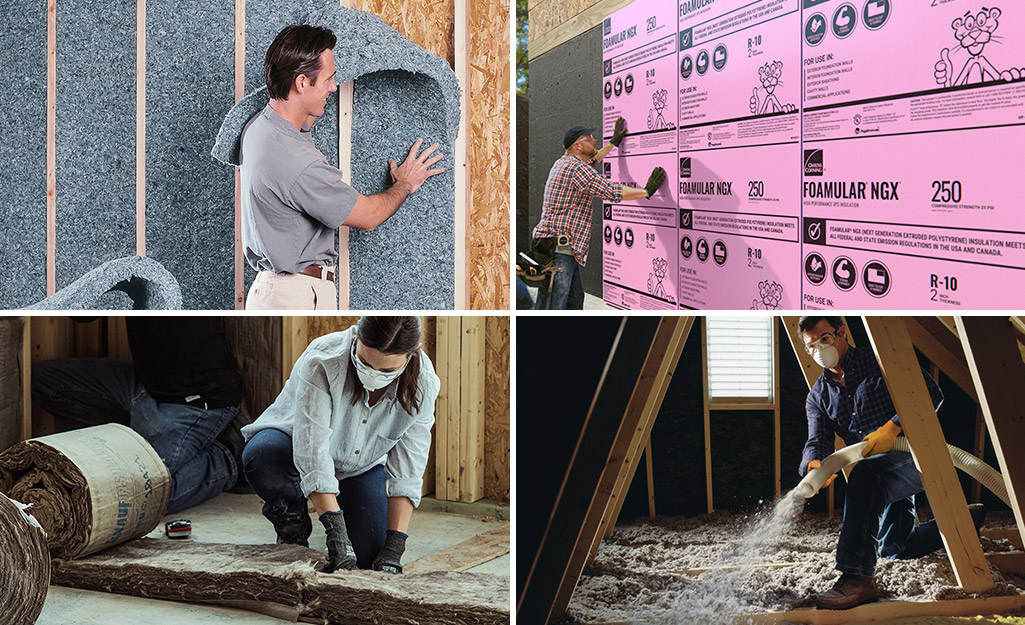

Fiberglass:
- Shorter lengths
- Available for various elbow and tee joints
- The most commonly used insulating material
Self adhesive foam insulation with aluminum foil backing:
- Effective where space is at a premium
- Suitable for hot and cold pipes
6 foot lengths of 3/8 inch tubular polyethylene foam:
- For use with long runs of pipe
- Pre-slit tubes come in different internal diameters
- Tubes snap into place quickly and easily on pipes from 1/4-inch iron to 1 1/4-inch copper
- Available as rubber tubes
Spray foam:
- Used for new installations
- Used for spot repairs and leak sealing
Duct insulation is measured in terms ofR-value, which is a measure of resistance to heat flow. The higher the R value, the better the degree of insulation.
Duct insulation ranges in thickness from 1 to 2 1/2 inches and provides an R-value of about R-4 per inch of thickness.
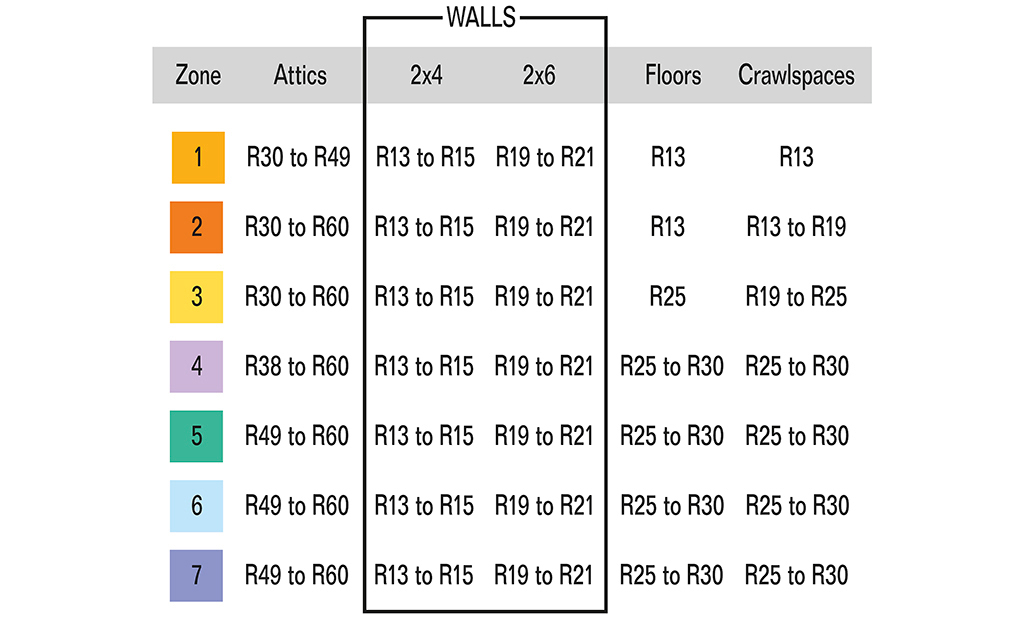
Warm Climate:
- R-Values for Unconditioned Attic: R-4 to R-8
- R-Values for Unconditioned Basement/Crawlspace: None to R-4
Mixed Climate:
- R-Values for Unconditioned Attic: R-4 to R-8
- R-Values for Unconditioned Basement/Crawlspace: R-2 to R-8
Cold Climate:
- R-Values for Unconditioned Attic: R-6 to R-11
- R-Values for Unconditioned Basement/Crawlspace: R-2 to R-11
Upkeep & Features
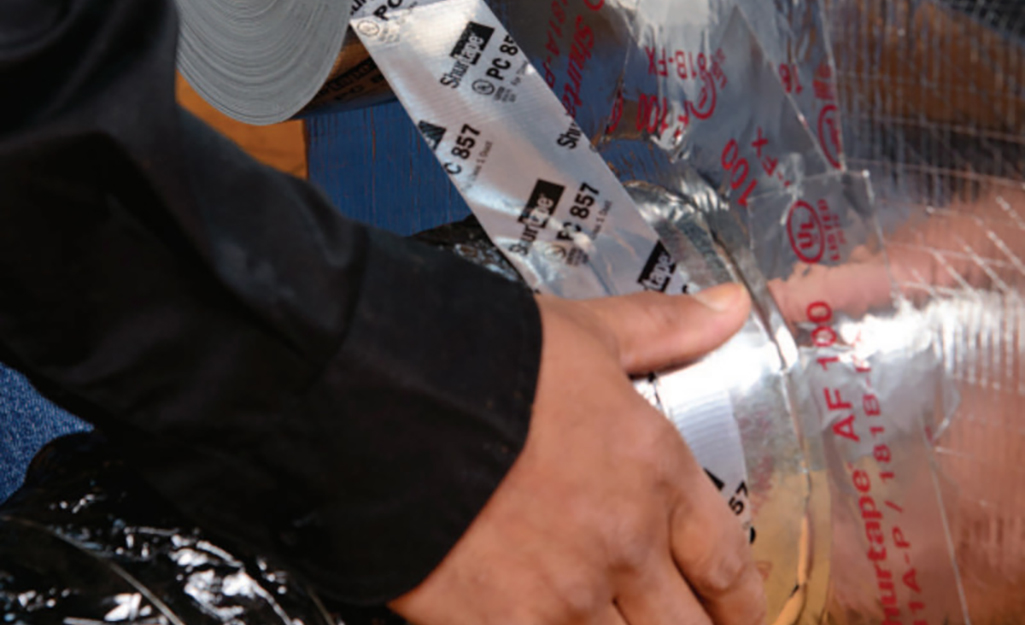

Leaky air ducts can raise a home’s heating and cooling costs by 20 percent to 40 percent, and can contribute to health issues. Keep an eye on duct leaks and clean the ducts if mold or excessive dust is present.
Duct Leaks:
- Look for air leaks in ductwork in unconditioned areas, like attics and crawlspaces.
- Check for separation in areas where sections join, and for obvious holes.
- If your duct joints have been sealed with cloth duct tape, look for cracks and loose or peeling tape.
- Small repairs are fairly easy to make, using duct mastic/sealant, mastic tape or high-quality duct tape approved for heating and air conditioning systems.
- Bigger repairs may need to be made by a professional. Contact The Home Depot’s Installation Services for more information.
Maintaining a Balanced System:
- Forced air distribution systems are designed to be a closed, pressure-balanced loop, with the same amount of air entering and leaving conditioned zones through the ductwork. Maintaining a balanced air system not only makes your home more comfortable, but also makes the system run more efficiently, which translates into lower utility bills.
- While a well-designed system should not need adjusting, if you find some rooms too hot and others too cold, you can tweak the balance yourself by adjusting levers on air registers and balancing dampers in rooms.
Cleaning air ducts periodically removes allergens like pollen as well as other contaminants like dust and dirt. Check debris accumulation in your ducts at least once a year and have them cleaned immediately for these reasons.
- Mold is visible
- Ducts are infested with vermin
- Ducts have excessive dust or dirt that is being released through supply registers
Cleaning techniques range from using a brush, rag and vacuum cleaner to remove loose dirt and dust on registers, grilles and duct walls to professional whole-house duct cleaning services that clean the entire HVAC system with services like duct sealing and biocide applications.
Feature to Consider:
- Decorative grilles and registers are available in a variety of materials and finishes and are an easy way to change your decor.
- In-line booster fans heat and cool air for increased comfort.
- Register vent boosters pull more air from registers and increase comfort in rooms that aren’t served by your HVAC system.
Knowing the different types of vents and ducts in your home will make you more knowledgeable when it's time to have them maintenanced. Use The Home Depot Mobile Appto have everything you need delivered right to your doorstep.