
Copper piping is joined together using flux and soldering. In the soldering process, heat is applied to the joint where the pipe and fitting meet. The gap between the joint is filled with molten metal. This guide identifies the types of solder available as well as the right flux for soldering your project.
Flux Types and Features
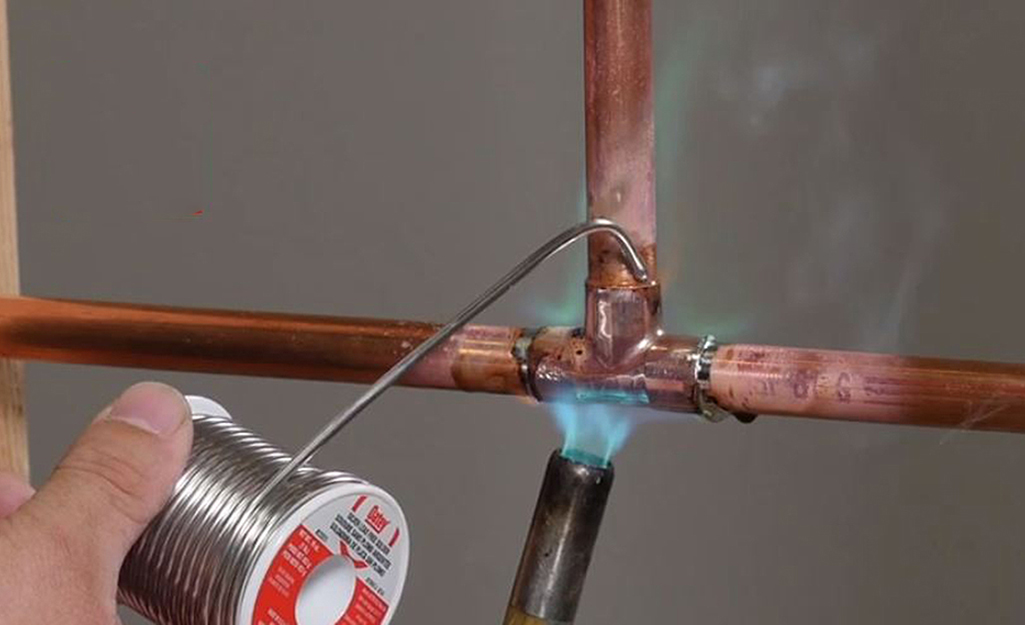
Solder flux is a chemical agent used to join and clean metals. It is made from organic or inorganic materials and is available in liquid and paste forms. The best soldering flux for your project depends on many factors and characteristics. Soldering and brazing are basically the same process, but brazing occurs at the temperature of the room or area it takes place.
Paste:
- Cleans and fluxes simultaneously.
- Lead-free.
- Removes surface oxidation from pipes.
- Can be used on all materials except aluminum and stainless steel.
Tinning Paste:
- Contains lead-free solder wire in powder form to clean and pre-tin the pipe surface, which allows solder to easily draw into the joint.
- Ideal for use with large diameter copper pipe; can withstand higher temperatures that ordinary flux cannot.
- Do not use on aluminum, magnesium or stainless steel.
- Do not use water soluble tinning paste or normal water soluble paste on electronics.
Hot Weather Formula Paste:
- Ideal for areas with high temperatures.
Water Soluble Paste:
- Cleans and fluxes simultaneously.
- Ideal for working with supply lines for drinking water, copper, fire sprinklers and hydronic heating systems.
- Meets plumbing code ASTM B-813 standards for flux used in potable water systems.
- Meets plumbing code requirements for water flushable fluxes.
Water Soluble Tinning Paste:
- Contains lead-free solder wire in powder form to clean and pre-tin copper pipe surfaces, which allows solder to easily draw into the joint.
- Won’t turn copper green.
- Meets ASTM B-813 standards and is approved for use by model plumbing code.
- Ideal for use with large diameter copper pipe.
- Little expertise needed for effective use.
Liquid:
- Cleans the surface of pipes and prepares them for solder.
- Features a strong cleaning agent which cleans oxidized copper.
- Allows for fast, effective soldering.
Soldering
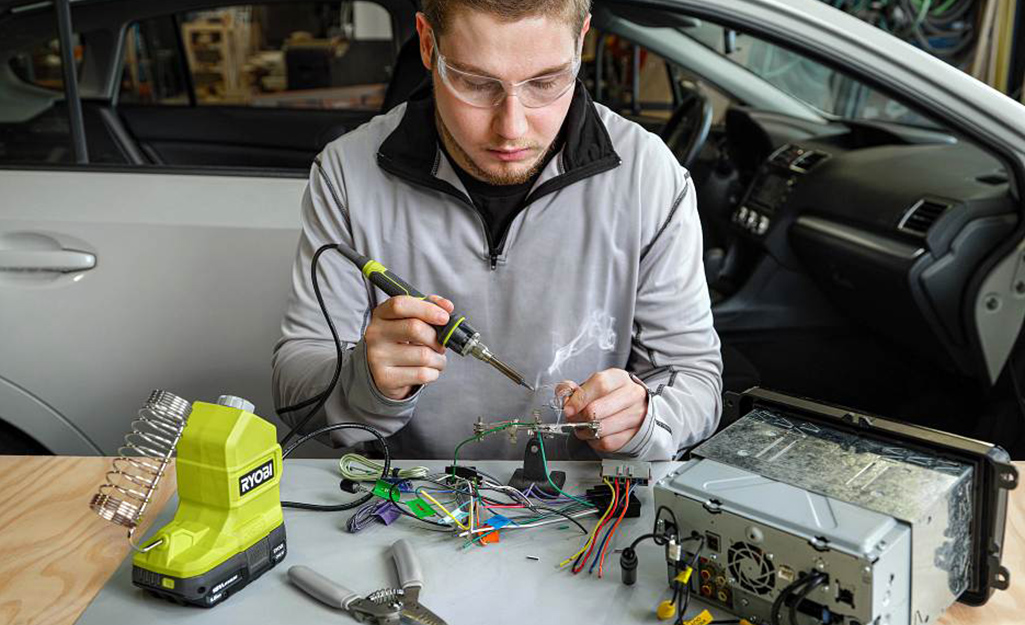

Solder is a metal alloy made up of different elements. A solder wire, and sometimes liquid solder, is used to join piping and make repairs. The U.S. Safe Water Drinking Act prohibits the use of leaded solders on lines carrying drinking water. Lead-free plumbing solders are required for use on pipes carrying drinking water, also known as potable water lines.
Leaded solders are available for applications that do not come into contact with potable water, such as sheet metal repair or copper drain lines.
Brazing
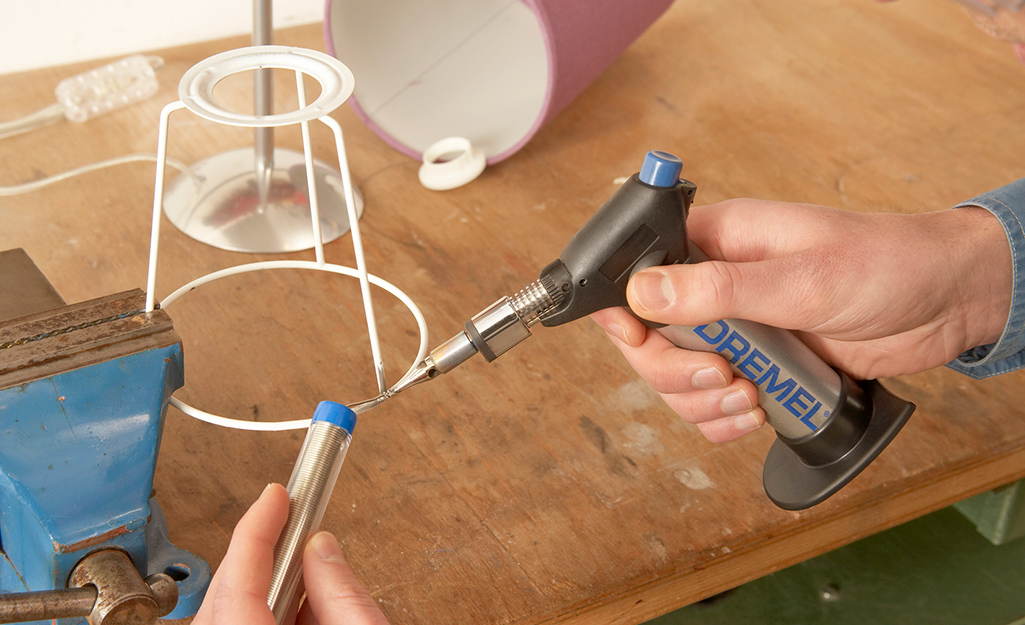

Brazing is another method for joining metal pipe pieces together. In general, soldering takes place at temperatures below 840 Fahrenheit, while brazing occurs at higher temperatures.
Brazing is used when high joint strength is required.
Hard solder, which is used for brazing, melts at higher temperatures and is available in various degrees of hardness.
Brazing requires a different kind of flux and solder. The flux is formulated to withstand the higher temperatures associated with brazing. The filler is a different combination of metals that melt at a higher temperature and are stronger when cooled.
Safety

Safety should always be the primary concern when soldering or brazing. Always use fire retardant personal protection equipment like a heat cloth or flame protection blanket when working around combustible elements like wood, drywall and insulation.
Other tips include:
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby at all times.
- Wear safety glasses, a helmet and protective gloves.
- Wash off excess flux after soldering to prevent corrosion.
- Do not use flux on electrical parts. Its acidity can lead to corrosion and short circuits.
- Use adequate ventilation when fluxing and soldering, particularly in close quarters.
- Always refer to a professional in your area for codes or additional safety tips.
Helpful Tools

When soldering, there are several tools such as tube cutters, flame protectors and emery cloths that make the work look professional and keep you safe while working.
Tube cutters: Help ensure smooth, even cuts when working with plastic tubing, minimizing the amount of time you’ll have to spend sanding, and ensuring a better solder.
Flame protector: If you’re heating a joint near combustible material, use a flame protector or heat shield to protect the heat-sensitive material from damage.
Deburring tool: Makes it much easier to remove burrs and rough edges from pipes once they’ve been cut.
Emery cloth: Use strips of emery cloth to clean and prepare copper pipes for the application of flux and solder.
Ready to find the supplies you need? Use The Home Depot Mobile App to help you locate products and check inventory, making it easier when you visit your local Home Depot store.






























